Page 28 - Science - 5
P. 28
Role of Nasal Cavityof Nasal Cavityof Nasal Cavity
Role
Role
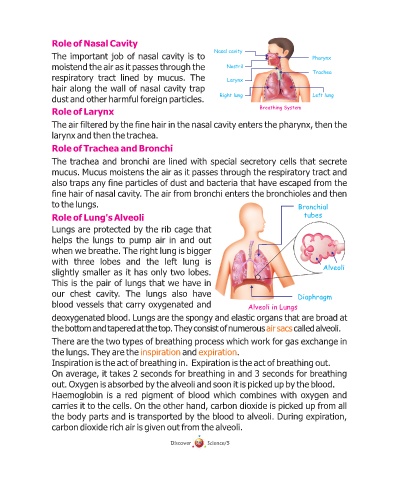
Nasal cavity
The important job of nasal cavity is to Pharynx
moistend the air as it passes through the Nostril
Trachea
respiratory tract lined by mucus. The Larynx
hair along the wall of nasal cavity trap
Right lung Left lung
dust and other harmful foreign particles.
Breathing System
Role of Larynx
Role of LarynxRole of Larynx
The air filtered by the fine hair in the nasal cavity enters the pharynx, then the
larynx and then the trachea.
Role of Trachea and Bronchi
Role
Role of Trachea and Bronchiof Trachea and Bronchi
The trachea and bronchi are lined with special secretory cells that secrete
mucus. Mucus moistens the air as it passes through the respiratory tract and
also traps any fine particles of dust and bacteria that have escaped from the
fine hair of nasal cavity. The air from bronchi enters the bronchioles and then
to the lungs. Bronchial
Role
Role tubes
Role of Lung's Alveoliof Lung's Alveoliof Lung's Alveoli
Lungs are protected by the rib cage that
helps the lungs to pump air in and out
when we breathe. The right lung is bigger
with three lobes and the left lung is
Alveoli
Alveoli
Alveoli
slightly smaller as it has only two lobes.
This is the pair of lungs that we have in
our chest cavity. The lungs also have Diaphragm
blood vessels that carry oxygenated and Alveoli in Lungs
deoxygenated blood. Lungs are the spongy and elastic organs that are broad at
the bottom and tapered at the top. They consist of numerous air sacs called alveoli.
There are the two types of breathing process which work for gas exchange in
the lungs. They are the inspiration and expiration .
Inspiration is the act of breathing in. Expiration is the act of breathing out.
On average, it takes 2 seconds for breathing in and 3 seconds for breathing
out. Oxygen is absorbed by the alveoli and soon it is picked up by the blood.
Haemoglobin is a red pigment of blood which combines with oxygen and
carries it to the cells. On the other hand, carbon dioxide is picked up from all
the body parts and is transported by the blood to alveoli. During expiration,
carbon dioxide rich air is given out from the alveoli.
Discover 29 Science/5
29
29